Thursday, 13 March 2025
A Major Step Towards Non-Invasive Diabetes Monitoring Using NFC Technology
ICN2 researchers have developed a portable, wireless biosensor for the detection of glucose in urine based on Prussian-blue nanoparticles.
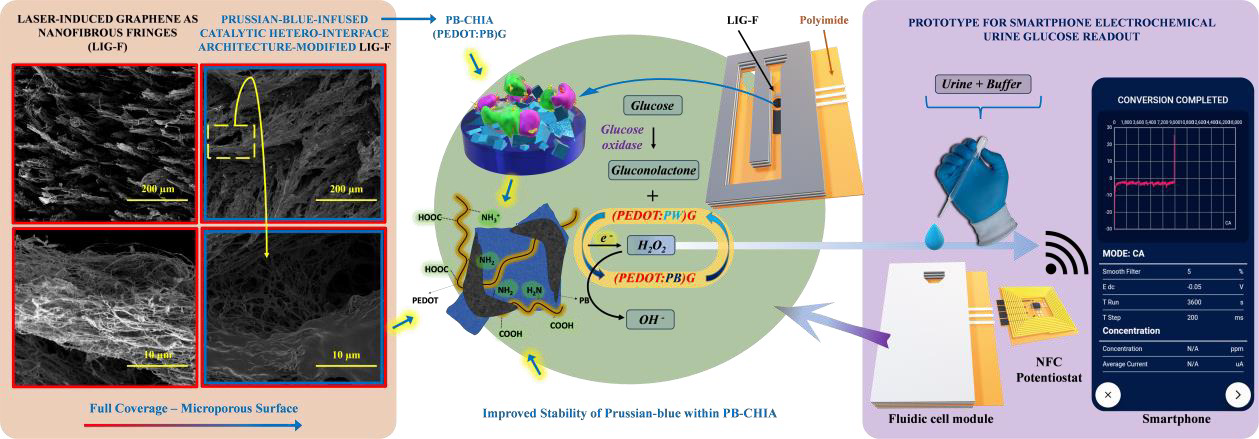
Monitoring glucose levels is essential for diabetes management. However, traditional methods, mainly based on blood analysis, can be invasive and uncomfortable. Recently, research led by Dr Sinan Uzunçar and ICREA Prof. Arben Merkoçi (ICN2 Nanobioelectronics and Biosensors Group) has developed an innovative wearable platform that enables non-invasive glucose detection in urine. This provides an easier and more comfortable alternative for diabetes patients. The results of the study have recently been published in Advanced Science.
The device is based on the use of Prussian-blue nanoparticles (PBNPs), a promising material for electrochemical applications. Its structure is further stabilised with a polymer (PEDOT) and gelatin, creating a catalytic surface that can be integrated into different types of electrodes and used as a biosensor. In addition, the device incorporates NFC technology, which allows glucose measurement results to be transmitted to a smartphone within seconds, without the need for batteries. The study confirmed that this method is highly sensitive for the detection of glucose in urine.
This achievement represents a significant advance in the development of portable, non-invasive clinical analysis platforms. The next steps before commercialisation will be clinical evaluation with real samples. In summary, these findings could pave the way for new systems to detect other diseases through urine analysis.
Reference article:
Uzunçar, S; Maroli, G; Urban, M; Merkoçi, A. Prussian-Blue Catalysis and NFC Synergy: a Battery-Free Laser-induced Graphene-Based Platform for Urine Glucose Monitoring at Point-of-Care. Advanced Science. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202500365.

