ICN2 researchers explore the potential applications of scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) for the real-time monitoring of electrocatalytic conversion reactions, making it a powerful tool for understanding and designing more efficient energy technologies.
The transition from fossil fuels to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources is one of today's major challenges. One of the most promising technologies in this area includes the electrocatalytic conversion of small molecules such as water or carbon dioxide, to produce green fuels and other valuable chemicals. This conversion would be carried out using electrical energy from sustainable sources. Although this is a key strategy in the transition to a more sustainable energy system, it is necessary to carefully design the catalytic materials that enable these reactions to improve their activity and efficiency.
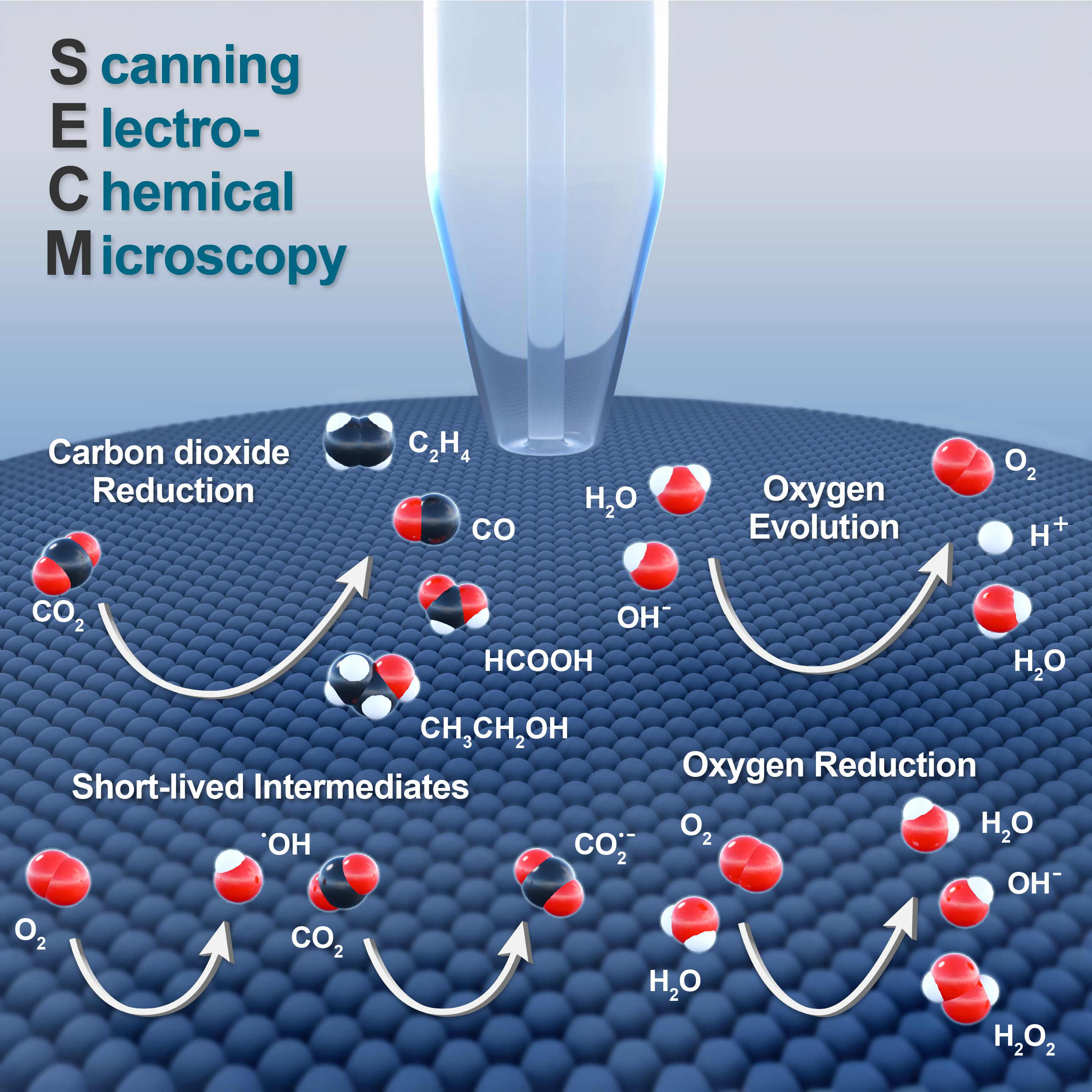
In this context, ICREA Prof. María Escudero-Escribano and PhD student Jaxiry Barroso from the ICN2 Nanoelectrocatalysis and Sustainable Chemistry Group have published a review article in the ChemCatChem journal. The article analyses how scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) enables real-time monitoring of key electrocatalytic processes such as carbon dioxide conversion and oxygen electrocatalysis, as well as the detection of short-lived intermediates.
These studies demonstrate the unique capability of this technique to detect and quantify both intermediates and products of the reaction, providing valuable insights into the complex dynamics at the electrode–electrolyte interface. The authors also highlight emerging applications where SECM can be coupled with complementary in situ techniques to provide both chemical and structural information.
In summary, the review underscores how incorporating SECM as an in-situ characterisation tool allows to guide the rational design of more efficient and selective catalysts—crucial for advancing sustainable energy conversion technologies.
Reference article:
In Situ Elucidation of Reaction Mechanisms in ElectrocatalysisUsing Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. Barroso-Martínez, JS; Escudero-Escribano, M. ChemCatChem. (2025). DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202500352

