Severo Ochoa Programme 2018-2022 Pillar 1: APPLICATION DOMAINS - Environment
Some ICN2 groups are beginning to branch out into the design and fabrication of sensors and biosensors for the detection and monitoring of environmental indicators like air, soil and water quality. Others are developing active nanostructures and devices with relevant properties for environmental remediation. For all these applications, high sensitivity and selectivity for a variety of relevant targets, fast turnaround times, portability and cost-effectiveness are important objectives.
Highlights
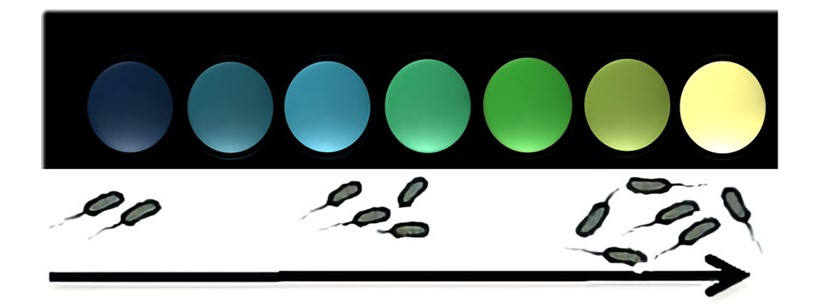
Biosensors for pollutant detection and monitoring
Progress has been made in the development of optical and electrochemical biosensors and their full integration in portable platforms for detecting bacterial contamination in water or food.
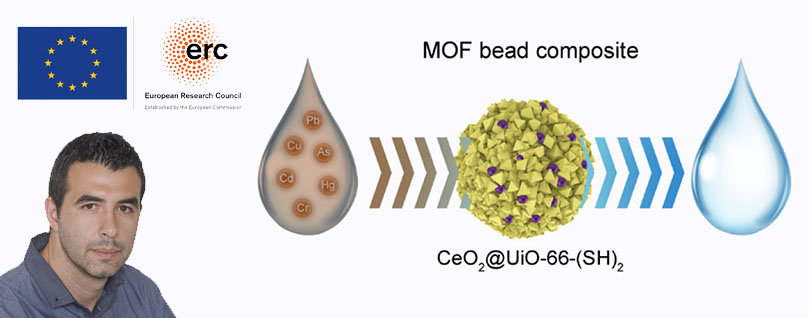
Pollutant removal and degradation
New composites based on Metal Organic Frameworks (MOF), inorganic nanoparticles and nanostructured materials have been developed for various applications:
- as catalysts for CO2 conversion (META2nol project) and as membranes for CO2 capture (GENESIS projects), for prototype development with CEMEX;
- for heavy metal removal (ERC Proof of Concept grant), including a patent and a collaboration for its exploitation with Lotus Partners;
- for water removal of pollutants and decontaminationNano-safety
Activities have been addressed to the study of nanoparticle immunosafety, ecotoxicity, and health effect assessment.
This newly established exploratory application domain will also address issues of nano-safety, safe-by-design and lifecycle assessment (incl. ecotoxicity studies), in recognition and vigilance of the potential negative impact of nanostructures and nano-interactions on the environment.
The key research priorities identified in this field are the development of sensor platforms for pollution detection and monitoring and of functional materials for pollutant removal and degradation. Nano-safety and life-cycle assessment are new topics that will be also investigated, including the ICN2’s socio-environmental responsibility in their regard.
The specific actions that will be taken include: forging new internal synergies to develop technologies for pollution detection and remediation; and organising one international workshop on these topics.
Dr María José Esplandiu
CSIC Tenured Scientist at the ICN2 Magnetic Nanostructures Group